研究概況


本實驗室研究方向集中在三個領域
 |
高分子 |
單聚高分子(homopolymers)與團聯式共聚高分子(block copolymers)的合成與鑑定 |
| |
|
|
 |
奈米 |
新穎奈米材料的製備與自組裝(self-assembly) |
| |
|
|
 |
能源 |
太陽能電池等方面的應用 |
| |
|
|
|
|
 |
研究獲媒體報導
感謝 民視 《台灣新視野》節目採訪,介紹我們實驗室「自修復纖維」的研究工作。
播出日期:2023 年 4 月 8 日(星期六)
Youtube 影片連結

高分子
高分子是具有長鏈的分子。
| 我 |
們 |
實 |
驗 |
室 |
, |
主 |
要 |
在 |
探 |
討 |
關 |
於 |
高 |
分 |
子 |
材 |
料 |
於 |
介 |
面 |
上 |
的 |
一 |
些 |
特 |
殊 |
現 |
象 |
, |
喜 |
| 愛 |
這 |
個 |
領 |
域 |
的 |
同 |
學 |
們 |
, |
歡 |
迎 |
加 |
入 |
我 |
們 |
實 |
驗 |
室 |
。 |
其 |
中 |
的 |
一 |
個 |
方 |
向 |
, |
就 |
是 |
作 |
| 高 |
分 |
子 |
的 |
奈 |
米 |
材 |
料 |
, |
因 |
為 |
當 |
高 |
分 |
子 |
被 |
製 |
備 |
在 |
奈 |
米 |
尺 |
度 |
的 |
時 |
後 |
, |
裡 |
面 |
的 |
高 |
| 分 |
子 |
鏈 |
就 |
會 |
因 |
為 |
受 |
限 |
效 |
應 |
的 |
關 |
係 |
, |
而 |
造 |
成 |
形 |
態 |
上 |
或 |
是 |
物 |
理 |
化 |
學 |
性 |
質 |
在 |
分 |
| 子 |
級 |
別 |
上 |
有 |
很 |
特 |
殊 |
的 |
變 |
化 |
。 |
在 |
這 |
個 |
方 |
向 |
, |
我 |
們 |
也 |
使 |
用 |
了 |
一 |
些 |
光 |
電 |
高 |
分 |
子 |
| , |
並 |
探 |
討 |
發 |
光 |
與 |
電 |
性 |
方 |
面 |
的 |
改 |
變 |
, |
對 |
於 |
實 |
驗 |
結 |
果 |
背 |
後 |
的 |
基 |
理 |
, |
我 |
們 |
已 |
經 |
| 隱 |
約 |
有 |
一 |
些 |
基 |
本 |
的 |
概 |
念 |
形 |
成 |
, |
但 |
是 |
還 |
有 |
很 |
多 |
特 |
殊 |
與 |
有 |
趣 |
的 |
問 |
題 |
與 |
答 |
案 |
埋 |
| 藏 |
不 |
同 |
的 |
觀 |
察 |
結 |
果 |
後 |
面 |
。 |
對 |
我 |
們 |
研 |
究 |
方 |
向 |
有 |
興 |
趣 |
的 |
同 |
學 |
, |
可 |
以 |
先 |
看 |
我 |
們 |
| 網 |
站 |
上 |
所 |
介 |
紹 |
的 |
研 |
究 |
簡 |
介 |
, |
要 |
看 |
我 |
們 |
近 |
期 |
的 |
發 |
表 |
成 |
果 |
, |
也 |
可 |
以 |
點 |
擊 |
發 |
表 |
| 頁 |
面 |
上 |
的 |
文 |
章 |
連 |
結 |
。 |
除 |
了 |
在 |
奈 |
米 |
尺 |
度 |
的 |
研 |
究 |
之 |
外 |
, |
我 |
們 |
也 |
對 |
高 |
分 |
子 |
材 |
料 |
| 在 |
較 |
大 |
尺 |
度 |
的 |
現 |
象 |
與 |
行 |
為 |
有 |
興 |
趣 |
, |
所 |
以 |
我 |
們 |
也 |
研 |
究 |
了 |
如 |
電 |
紡 |
絲 |
等 |
方 |
法 |
。 |
| 這 |
個 |
方 |
法 |
可 |
以 |
用 |
來 |
製 |
備 |
奈 |
米 |
到 |
微 |
米 |
尺 |
度 |
的 |
高 |
分 |
子 |
纖 |
維 |
, |
要 |
控 |
制 |
這 |
些 |
纖 |
維 |
| 裡 |
面 |
的 |
特 |
性 |
與 |
形 |
態 |
, |
可 |
以 |
改 |
變 |
電 |
紡 |
絲 |
的 |
條 |
件 |
, |
或 |
是 |
可 |
利 |
用 |
後 |
處 |
理 |
的 |
方 |
法 |
| 。 |
最 |
近 |
, |
我 |
們 |
也 |
開 |
始 |
使 |
用 |
3 |
D |
列 |
印 |
的 |
概 |
念 |
, |
用 |
來 |
製 |
造 |
更 |
大 |
尺 |
度 |
的 |
材 |
料 |
。 |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
高分子奈米材料 ( Hierarchical Polymer Nanomaterials ) |
|
| |
|
|
|
We explore hierarchical nanostructures based on one-dimensional materials. An obstacle to the wide-spread use of hierarchical nanostructures is the difficulty in controlling the surface properties of the structures because of unclear and uneven surface patterns. We introduce a noval technique to create hierarchical nano rod arrays by utilizing both polymer microspheres and porous anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) templates. Wet polymer microspheres are placed on the templates where they are drawn into the nanopores. Nanorods are created in the nanopores and released into a NaOH(aq) solution. Then the microspheres settled into various layers in a 2D hexagonal array. The AAO template generate s a second scale of ordering with hexagonally packed pores. This research shows that ordering on two different size scales can be controlled by changing the size of the microsphere and pores sizes of AAO templates. A technique that allows such control is important to manipulating key surface properties during the fabrication process. This innovative approach to polymer science is making the precise control and fabrication of novel nanostructures with desired properties a reality. |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
| |
實驗室研究關鍵字 |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
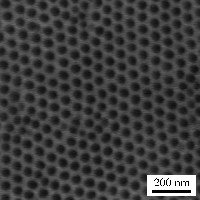
陽極氧化鋁模板 ( Anodic Aluminum Oxide Template) |
| |
|
|
Anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) template is prepared electrochemically from aluminum metal. The popularity of the AAO template is because of its exceptional thermal stabilities, ease of fabrication, and its versatility as far as controlling the pore diameter and pore length. The AAO template is widely used for the formation of metallic and semiconductor nanowires, and even carbon nanotube transistors. The AAO templates typically contain high porosities, and the pores are arranged in a hexagonal array. These templates can be created with uniform pore sizes and distributions . The dimension of the templ at e s can be tuned by us ing different anodization conditions |
| |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
| |
|
|
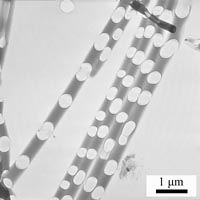
不穩定性導致的新穎高分子結構 (Novel Polymeric Stuctures Induced by Instabiliies) |
| |
|
|
We study on thin film instabilities in confined channels . T he thermal properties of one-dimensional nanostructures are investigated . We prepare t hin films of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) by filling cylindrical nanopores in an anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) membrane with a PMMA solution. When the PMMA nanotubes were altered because of a change in temperature, waves in the film thickness formed and were induced by Rayleigh instability. The amplitude of the waves increased over time and bridged across the nanopore in the membrane, resulting in the formation of hole-containing polymer nanorods. The same result was observed when PMMA films were confined within carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The Rayleigh instabilities in these structures offer an innovative way to manipulate and to create polymer nanostructures, and the nanorods may have potential applications such as optical sensors or drug delivery devices. |
| |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
階級性高分子奈米材料 ( Hierarchical Polymer Nanomaterials ) |
|
| |
|
|
|
We explore hierarchical nanostructures based on one-dimensional materials. An obstacle to the wide-spread use of hierarchical nanostructures is the difficulty in controlling the surface properties of the structures because of unclear and uneven surface patterns. We introduce a noval technique to create hierarchical nano rod arrays by utilizing both polymer microspheres and porous anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) templates. Wet polymer microspheres are placed on the templates where they are drawn into the nanopores. Nanorods are created in the nanopores and released into a NaOH(aq) solution. Then the microspheres settled into various layers in a 2D hexagonal array. The AAO template generate s a second scale of ordering with hexagonally packed pores. This research shows that ordering on two different size scales can be controlled by changing the size of the microsphere and pores sizes of AAO templates. A technique that allows such control is important to manipulating key surface properties during the fabrication process. This innovative approach to polymer science is making the precise control and fabrication of novel nanostructures with desired properties a reality. |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
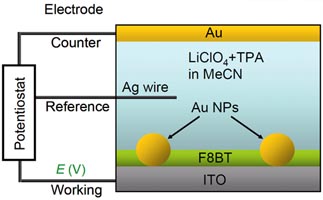
電致化學發光 (Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence (ECL)) |
|
| |
|
|
We study the electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) of polyflourenes , a class of polymer materials that is used in making light emitting diodes display. Chemiluminescence is the emission of light as a result of a chemical reaction at environmental temperatures, usually involving an electron transfer reaction. G old nanoparticles are used as initiators in the ECL reaction process by creating leaks. ECL waves formed from the leaks and were determinative of whether the transport process would cease or continue. |
|
| |
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
| |
| 其中一個太陽能電池研究發展的主要方向,是利用共軛高分子(conjugated polymers)來作為主要材料的有機太陽能電池(organic solar cells)。共軛高分子一般具有較高的光吸收係數,其光電性質可以藉由改變其化學結構而輕易地調整。這一類型的太陽能電池元件,可利用旋轉塗佈(spin coating)等方式來製造,因此可降低其製作成本。除了有機太陽能電池之外,共軛高分子也被應用於其他種類的有機光電元件,例如有機場效電晶體(organic field effect transistors, OFETs)或是有機發光二極體(organic light-emitting diodes, OLED)等。<更多> |
|
| |
|
| |
|
高分子電紡織纖維(Polymer Fibers by Electrospinning)
實驗室研究關鍵字: 高分子、奈米、不穩定
|